8th Grade Science Standards
EIGHTH GRADE: OVERVIEW
The academic standards for eighth grade establish the content knowledge and skills for Tennessee
students necessary to prepare them for the rigorous levels of higher education and future job markets.
The course provides students with a wealth of experiences for both science practices and content
knowledge. The academic standards for science in eighth grade are research-based and supported by
the National Research Council’s Framework for K-12 Science Education.
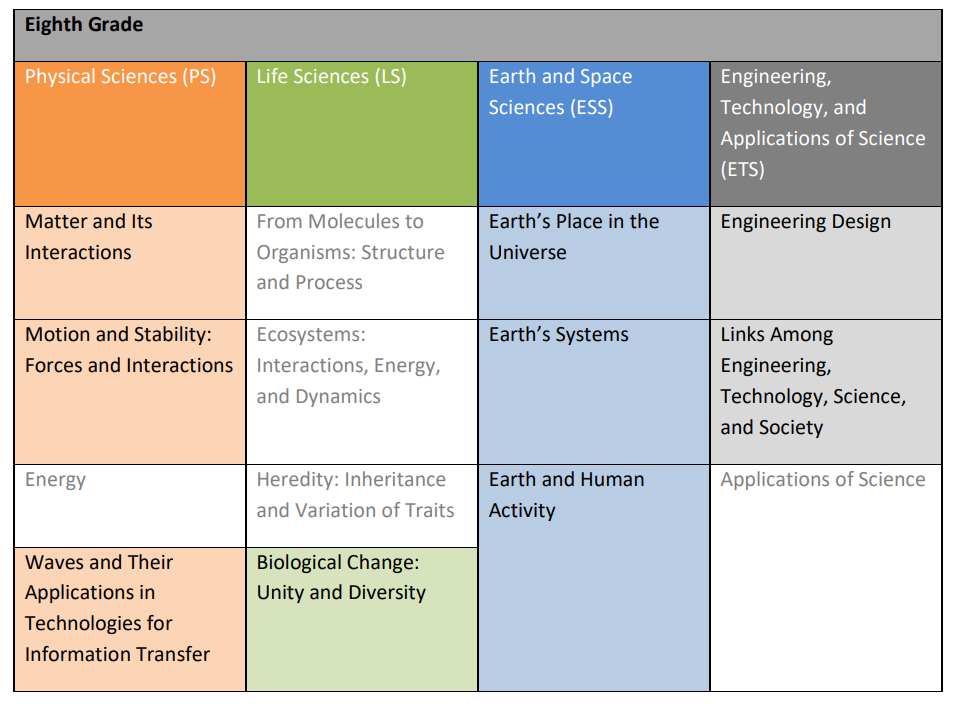
The academic standards herein establish the core content and practices of science and engineering, as
well as what Tennessee students need to know by the end of eighth grade. Disciplinary core ideas for
eighth grade include:
The standards incorporated into this grade have been streamlined for the students’ K-12 coherent
experience for a diversity of learners. The themes for science in eighth grade are how forces and motion
drive objects in our solar systems (ESS1), move lithospheric plates (ESS2), and how nature’s driving
forces of geology (ESS2) impact ecosystems via environmental selection for a species (LS4). This content
utilizes core ideas from sixth and seventh grade; for example, using a hereditary approach in seventh
grade to examine natural selection in eighth grade. Tennessee's state mathematics standards are
integrated into the science standards, specifically forces and motion (8.PS2). Special attention is given to
science literacy through the use of the science and engineering practices. Students are often required to
gather information from reliable sources to construct evidenced-based arguments (e.g., 8.ESS2).
By the end of eighth grade, it is expected that students should be able to demonstrate the skills and content knowledge emphasized in the following standards in preparation for future learning in science
and its practice.
EIGHTH GRADE: ACADEMIC STANDARDS
8.PS1: Matter and Its Interactions
1) Use a model to understand that atoms are a system composed of a positively charged nucleus
surrounded by one or more negatively charged particles called electrons.
2) Develop a model to explain how the light coming from distant stars and the formation of
heavier atoms is the result of changes in the composition of the nucleus of the atom and the
energy released during the process of nuclear fusion.
8.PS2: Motion and Stability: Forces and Interactions
1) Conduct an investigation to provide evidence that the size of force fields (electric and magnetic)
depends on the magnitudes of the charges, current, or magnetic strengths involved and the
distances between interacting objects.
2) Ask scientific questions about data to determine how manipulating variables can increase or
diminish the electric current and magnetic field strength in electromagnets, generators, and
electric motors.
3) Construct an argument using evidence to support the claim that gravitational interactions in a
large-scale system (e.g., galaxies and solar system) are attractive and depend on the masses of
and distance between interacting objects.
4) Construct an explanation to describe why the position and motion of object(s) in a system, and
the effects of forces on those objects, vary with respect to the observer.
5) Plan and conduct an investigation to provide evidence that the change in an object's motion
depends on the sum of the forces on the object and the mass of the object.
6) Evaluate and interpret that for every force exerted on an object there is an equal force exerted
in the opposite direction.
8.PS4: Waves and Their Applications in Technologies for Information
Transfer
1) Develop and use models to represent the basic properties of waves in a system including
frequency, amplitude, wavelength, and speed.
2) Construct explanations from observed patterns of wave behaviors to compare and contrast
mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves based on refraction, reflection, transmission,
absorption, and their behavior through a vacuum and/or various media.
3) Engage in argument from evidence to support the claim that digitized signals, sent as wave
pulses, are more reliable than analog signals to transmit information in a system.
8.LS4: Biological Change: Unity and Diversity
1) Using evidence from the geologic timescale, analyze and interpret data for patterns in the fossil
record that document the existence, diversity, extinction, and change in life forms throughout
Earth's history.
2) Construct an explanation addressing similarities and differences of the anatomical structures
and genetic information between extinct and extant organisms using evidence of common
ancestry and patterns between taxa.
3) Construct an explanation based on evidence that explains how genetic variations of traits in a
population increase some individuals' probability of surviving and reproducing.
4) Develop a scientific explanation of how natural selection plays a role in determining the survival
and reproduction of a species in a changing environment.
5) Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the technologies that have changed the
way humans use artificial selection to influence the inheritance of desired traits in other
organisms.
8.ESS1: Earth’s Place in the Universe
1) Research, analyze, and communicate that the universe began with a period of rapid expansion
using evidence from the motion of galaxies (i.e., redshift and blueshift), elemental
concentrations of hydrogen and helium, and cosmic background radiation.
8.ESS2: Earth’s Systems
1) Analyze and interpret data to support the assertion that rapid or gradual geographic changes
lead to drastic population changes and extinction events.
2) Evaluate data collected from seismographs to create a model of Earth's structure and to
understand how energy is derived from Earth's hot interior.
3) Gather and evaluate evidence that energy from the earth's interior drives convection cycles
within the asthenosphere which creates changes within the lithosphere including plate
movements, plate boundaries, and sea-floor spreading.
4) Construct a scientific explanation using data that explains the gradual process of plate tectonics
accounting for (a) the distribution of fossils on different continents, and (b) continental and
ocean floor features (i.e., mountains, volcanoes, faults, and trenches).
8.ESS3: Earth and Human Activity
1) Collect data, map, and describe patterns in the locations of volcanoes and earthquakes related
to tectonic plate boundaries, interactions, and hotspots in order to forecast the locations and
likelihoods of future events.
8.ETS1: Engineering Design
1) Use a model of a device that incorporates an electromagnet to test solutions to a design
problem with specific criteria and constraints.
8.ETS2: Links Among Engineering, Technology, and Applications of
Science
1) Research and communicate information to describe how data from technologies (e.g.,
telescopes, satellites, space probes, seismographs) provide information about Earth and objects
in space and how those scientific discoveries have in turn led to improved technologies.